Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ion complex; Presence of a Rh
ion complex; Presence of a Rh Intermediate in Direct Photoreduction
Intermediate in Direct PhotoreductionSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Yomogida, Takumi; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 126(12), p.5607 - 5616, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:13.38(Chemistry, Physical)The reaction mechanism of the direct photoreduction of a Rh ion complex to a Rh
ion complex to a Rh species induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser irradiation was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS) spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points and suggested that more than two Rh
species induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser irradiation was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure (DXAFS) spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points and suggested that more than two Rh species contribute toward the direct photoreduction of Rh
species contribute toward the direct photoreduction of Rh . Analysis of the time-resolved XANES data by singular value deposition showed that the direct photoreduction involves three Rh
. Analysis of the time-resolved XANES data by singular value deposition showed that the direct photoreduction involves three Rh species. Multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares analysis (MCR-ALS) of the time-resolved XANES data gave pure spectra and concentration profiles of the three Rh
species. Multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares analysis (MCR-ALS) of the time-resolved XANES data gave pure spectra and concentration profiles of the three Rh species. The Rh
species. The Rh species were assigned to Rh
species were assigned to Rh , Rh
, Rh , and Rh
, and Rh species based on the features of the pure XANES spectra. The concentration profiles suggested that the direct photoreduction proceeds in the order of Rh
species based on the features of the pure XANES spectra. The concentration profiles suggested that the direct photoreduction proceeds in the order of Rh
 Rh
Rh
 Rh
Rh . A reaction mechanism, which was proposed involving photoreductions of Rh
. A reaction mechanism, which was proposed involving photoreductions of Rh and Rh
and Rh , photoinduced autocatalytic reductions of Rh
, photoinduced autocatalytic reductions of Rh and Rh
and Rh , and photooxidation of Rh
, and photooxidation of Rh , well reproduced the concentration profiles of three Rh
, well reproduced the concentration profiles of three Rh species.
species.
Saeki, Morihisa; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakashima, Nobuaki*; Oba, Hironori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Pd in high-level radioactive wastes using laser-induced particle formation
Pd in high-level radioactive wastes using laser-induced particle formationYomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho; Saeki, Morihisa; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Esaka, Fumitaka; Oba, Hironori; Magara, Masaaki
no journal, ,
 Pd contained in high-level radioactive wastes (HLW) is a long-lived fission product. The procedure for
Pd contained in high-level radioactive wastes (HLW) is a long-lived fission product. The procedure for  Pd determination in HLW is demanded for safety assessment of geological disposal. Radiation measurement is difficult due to very low energy of beta radiation of
Pd determination in HLW is demanded for safety assessment of geological disposal. Radiation measurement is difficult due to very low energy of beta radiation of  Pd. Chemical separations and mass spectrometry methods are superior to the radiation measurement, but it has some problems on complicated analysis processes and
Pd. Chemical separations and mass spectrometry methods are superior to the radiation measurement, but it has some problems on complicated analysis processes and  Ag isobar contamination. We performed a novel procedure for
Ag isobar contamination. We performed a novel procedure for  Pd determination by laser-induced particle formation to overcome those problems. In this study, Pd separation by laser-induced particle formation was applied to the analysis of simulated HLW solutions. ICP-MS measurements demonstrated that the recovery ratio of Pd depended on solutions and ethanol concentrations in laser irradiation. The low contamination ratio indicated the high elemental selectivity of laser-induced particle formation.
Pd determination by laser-induced particle formation to overcome those problems. In this study, Pd separation by laser-induced particle formation was applied to the analysis of simulated HLW solutions. ICP-MS measurements demonstrated that the recovery ratio of Pd depended on solutions and ethanol concentrations in laser irradiation. The low contamination ratio indicated the high elemental selectivity of laser-induced particle formation.
 Pd in HLW with ICP-MS
Pd in HLW with ICP-MSYomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho; Saeki, Morihisa; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Esaka, Fumitaka; Oba, Hironori; Magara, Masaaki
no journal, ,
Inventory estimation of long-lived fission products (LLFPs) in high-level radioactive waste (HLW) is indispensable for the long-term safety assessment of geological repository. Reliability of the estimated inventory is verified with actual measurement values which are drawn from proven analytical techniques. There has been increasing interest in the development of new determination methods of Pd-107 which is one of the LLFPs with a half-life of 6.5 10
10 y because little measured data has been reported. Major difficulty in determination of Pd-107 involves the poor recovery of Pd in separation step required prior to measurement. In this study, a highly selective separation technique based on laser-induced microparticle formation has been applied to Pd separation. The recovery percentage of Pd from a simulated HLW solution were affected by irradiation time and laser pulse energy. The maximum recovery percentage of 60% was achieved by 20-min irradiation at the energy of 100 mJ.
y because little measured data has been reported. Major difficulty in determination of Pd-107 involves the poor recovery of Pd in separation step required prior to measurement. In this study, a highly selective separation technique based on laser-induced microparticle formation has been applied to Pd separation. The recovery percentage of Pd from a simulated HLW solution were affected by irradiation time and laser pulse energy. The maximum recovery percentage of 60% was achieved by 20-min irradiation at the energy of 100 mJ.
 Pd in radioactive wastes with mass spectrometry
Pd in radioactive wastes with mass spectrometryYomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho; Saeki, Morihisa; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Esaka, Fumitaka; Oba, Hironori; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
Palladium-107, which is one of the long-lived fission products in high-level radioactive waste (HLW), is a pure beta emitter with a half-life of 6.5 10
10 y. The inventory estimation of
y. The inventory estimation of  Pd is demanded for the long-term safety assessment of geological repository. ICP-MS is suitable for the determination of
Pd is demanded for the long-term safety assessment of geological repository. ICP-MS is suitable for the determination of  Pd because radiometry with a low beta energy of 33 keV is practically inapplicable. However, cumbersome chemical separation accompanied with highly radioactive sample treatment is still necessary prior to the measurement with ICP-MS. To minimize radioactive contamination and radiation exposure, simplified procedure is desirable. In this study, a simple separation technique based on laser-induced microparticle formation has been applied to Pd separation in a simulated HLW solution. Sufficiently high decontamination factors of coexisting elements (
Pd because radiometry with a low beta energy of 33 keV is practically inapplicable. However, cumbersome chemical separation accompanied with highly radioactive sample treatment is still necessary prior to the measurement with ICP-MS. To minimize radioactive contamination and radiation exposure, simplified procedure is desirable. In this study, a simple separation technique based on laser-induced microparticle formation has been applied to Pd separation in a simulated HLW solution. Sufficiently high decontamination factors of coexisting elements ( 1000) were observed, indicating that the proposed method achieved highly-selective separation of Pd.
1000) were observed, indicating that the proposed method achieved highly-selective separation of Pd.
 Pd with ICP-MS
Pd with ICP-MSYomogida, Takumi; Asai, Shiho; Saeki, Morihisa; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Esaka, Fumitaka; Oba, Hironori; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
no journal, ,
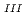 ion complexes; Extraction of intermediates information by multivariate spectral analysis
ion complexes; Extraction of intermediates information by multivariate spectral analysisSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Yomogida, Takumi; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
no journal, ,
The precious metal (PM) ions complexed with negative ions and water molecules in solution has a charge transfer absorption band in the UV region. When alcohol is added to such a PM complex solution and irradiated with an ultraviolet laser, the PM
complex solution and irradiated with an ultraviolet laser, the PM complex is electronically excited and reacts with the alcohol to be reduced to the neutral atom PM
complex is electronically excited and reacts with the alcohol to be reduced to the neutral atom PM . The reduced PM
. The reduced PM spontaneously aggregates in the solution to form fine particles. This process is called Laser-Induced Particle Formation (LIPF), and is used for the formation of precious metal nanoparticles and the recovery of precious metals from factory effluents. We have investigated the LIPF reaction mechanism of Rh
spontaneously aggregates in the solution to form fine particles. This process is called Laser-Induced Particle Formation (LIPF), and is used for the formation of precious metal nanoparticles and the recovery of precious metals from factory effluents. We have investigated the LIPF reaction mechanism of Rh ion complexes by in situ energy-dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy(XAFS). As a result of analyzing the obtained XAFS spectra, we found that Rh species with three oxidation numbers are involved in the Rh
ion complexes by in situ energy-dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy(XAFS). As a result of analyzing the obtained XAFS spectra, we found that Rh species with three oxidation numbers are involved in the Rh reduction reaction, which proceeds from Rh
reduction reaction, which proceeds from Rh to Rh
to Rh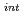 (intermediate) to Rh
(intermediate) to Rh .
.
 ion complex in a H
ion complex in a H O/EtOH solution
O/EtOH solutionSaeki, Morihisa*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Yomogida, Takumi; Tsuji, Takuya; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Oba, Hironori*
no journal, ,
The reaction mechanism of the direct photo-reduction of a Rh ion complex to a Rh
ion complex to a Rh species was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points. It suggested that more than two Rhn+ species contribute toward the reaction. We applied singular value deposition to the time-resolved XANES data and showed the contribution of three Rh
species was studied using dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) showed the absence of isosbestic points. It suggested that more than two Rhn+ species contribute toward the reaction. We applied singular value deposition to the time-resolved XANES data and showed the contribution of three Rh species to the direct photoreduction. Next, in order to extract spectral information on the Rh
species to the direct photoreduction. Next, in order to extract spectral information on the Rh intermediate, we analyzed the time-resolved XANES data using multivariate curve resolution analysis, which gives pure spectra and concentration profile of the Rh
intermediate, we analyzed the time-resolved XANES data using multivariate curve resolution analysis, which gives pure spectra and concentration profile of the Rh species. Finally, based on feature of the pure spectrum, we assigned the Rh
species. Finally, based on feature of the pure spectrum, we assigned the Rh intermediate to the Rh
intermediate to the Rh species.
species.